Installing the myDBR Application
To install the myDBR application manually, complete the following steps. (Note: myDBR also includes an automated installation wizard, which can be launched by pointing your browser to the mydbr/ directory.)
- Download the application
- Set up the database
- Install the PHP loader
- Install the application
Download the myDBR Application
Download the myDBR package from the myDBR website. Extract the contents of the ZIP file and place them within your web server's root directory.
Database User Configuration
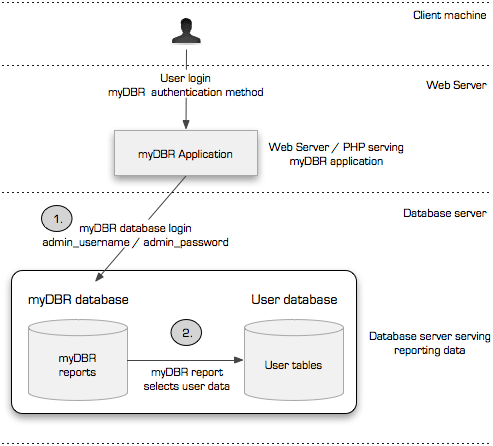
When you first launch myDBR, you will be prompted for the database credentials under which the application will operate. The provided database user must have the following permissions:
- Full access to the reporting database (default:
mydbr). - Select access to the database(s) containing the data you wish to report on (user database).
You can use an existing database account or create a new one. The following example demonstrates creating a dedicated mydbr user in MySQL:
$ mysql -uroot -p --default-character-set=utf8mb4
Enter password: ******
mysql> create user 'mydbr'@'localhost' identified by 'mydbr_password';
mysql> exit;
For SQL Server and SAP ASE, create the database with the mydbr user as the owner (or assign the db_owner role). Then, grant read access to your data databases (e.g., via the db_datareader role).
If you cannot create new users, ensure your existing user has the necessary privileges assigned.
Preparing the Reporting Database
myDBR stores all reporting metadata, including reports and internal objects, in a dedicated database. While we recommend using a separate database (e.g., mydbr), you can install these objects into your existing data database if necessary. All myDBR-specific items are prefixed with mydbr to distinguish them from your own data.
myDBR requires full access to its own reporting database and select access to the data source databases. You can use an existing database user or create a new one, such as the mydbr user created in the previous step.
Navigate to the install/db_creation directory to access the database creation scripts:
$ cd install/db_creation
MySQL
- Create the
mydbrdatabase (or use an existing one):
$ mysql -uroot -p --default-character-set=utf8mb4
Enter password: ******
mysql> create database mydbr character set = 'utf8mb4';
mysql> exit
- Grant the required privileges to the
mydbruser. In this example, our data resides inmydatabase:
$ mysql -uroot -p --default-character-set=utf8mb4
Enter password: ******
mysql> grant all on mydbr.* to 'mydbr'@'localhost';
mysql> grant select on mydatabase.* to 'mydbr'@'localhost';
mysql> exit
- Initialize the myDBR reporting database objects:
$ mysql -umydbr -p --default-character-set=utf8mb4 mydbr < mydbr_create_mysql.sql
Enter password: ******
Microsoft SQL Server
Create a database named mydbr using SQL Server Management Studio with the mydbr user as the owner. Then, initialize the database objects:
C:\>osql -n -U mydbr -P password -d mydbr < mydbr_create_mssql.sql
Ensure the user has sufficient privileges to create database objects.
SAP ASE
Create a database named mydbr using the SAP administration tools with the mydbr user as the owner. Then, initialize the database objects:
isql -Umydbr -Ppassword -Dmydbr < mydbr_create_SAP.sql
Ensure the user has sufficient privileges to create database objects.
Note: The installation script creates a default administrator account with the username
dbaand passworddba. You must change these credentials immediately after installation.
Installing the myDBR Files
The final step is to move the unpacked mydbr/ directory to your web server's root and configure the necessary permissions.
- Move the
mydbr/directory into your server's document root. - Ensure that the web server owns the files, or has at least read access to them.
- Ensure the
config.phpfile is writable by the web server. This allows administrators to manage settings via the browser. Ensure this file is not readable by other system users. - Upon first launch (by navigating to the myDBR URL in your browser), the application will prompt for connection details. The database credentials used here must have ownership of the myDBR database and access to the reporting data.
Example Permissions (Linux)
Adjust the commands below based on your specific document root and web server user (e.g., _www on macOS):
$ sudo mv mydbr /var/www/html
$ cd /var/www/html/mydbr
$ sudo chown -R apache:apache .
$ sudo chmod -R go-r .
$ sudo chmod -R u+w .
Navigate to your myDBR installation URL. If the files are correctly placed, you will be greeted by the setup screen.
Tip: If you need to restart the installation process, the
config.phpfile contains aSETUPDONEkey. Setting this tofalse(or removing the line) will cause myDBR to display the installation screen instead of the login page.
Installation Wizard
The installation wizard guides you through the initial configuration. myDBR automatically verifies your environment during this process. If any errors are displayed, resolve them before proceeding.
- Database Vendor: Select your database type. myDBR uses native drivers for optimal performance.
- Host: The hostname or IP address of your database server.
- Database: The name of the database containing the myDBR objects.
- Username: The database user created for myDBR (e.g.,
mydbr). This user must have permissions to execute stored routines. - Password: The password for the database user.
- Use SSL (MySQL only): Enables encrypted communication between the web server and the database. You can also specify client certificates for enhanced security.
- Key File: The client's private key (required when using certificates).
- Certificate: The client's security certificate.
- CA Cert: The Certificate Authority certificate.
After completing the setup, you can log in using the default credentials: username dba and password dba. Change these credentials immediately after your first login.