How Does myDBR Access the Database?
myDBR is designed to function as a reporting layer that requires minimal to no modifications to your data source databases. By default, myDBR installs its own schema (typically named mydbr) to store reports, user permissions, and internal configuration. The application only requires read access to the databases containing your reporting data.
You can also install myDBR directly into your existing data database. myDBR uses a unique naming convention to prevent conflicts: tables are prefixed with mydbr_, internal procedures with sp_MyDBR_, and report procedures with sp_DBR.
Database interaction occurs in two distinct phases: User Login and Report Execution.
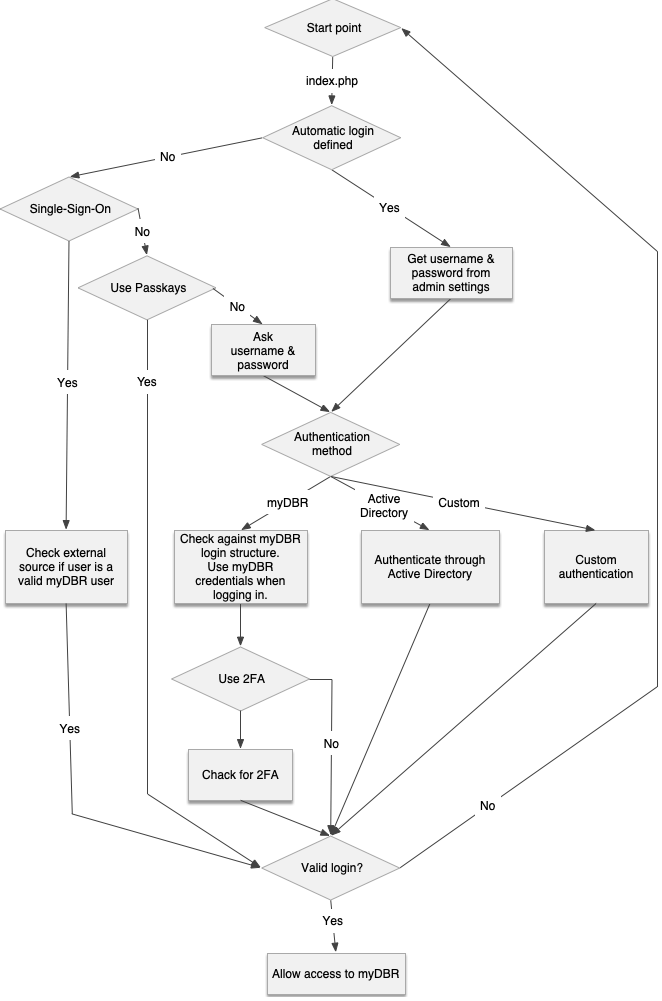
User Login
During the login process, myDBR verifies the user's credentials. Several authentication modules are available via the administration preferences:
- myDBR Authentication: Usernames and hashed passwords are stored internally within the
mydbr_userlogintable. - Single Sign-On (SSO): Authenticates users against an external application. For more details, see the Single Sign-On section.
- Active Directory / LDAP: Authenticates users against a local Microsoft Active Directory or Azure AD OpenID.
- Custom Authentication: Suitable for environments where myDBR should delegate authentication to an external service but SSO is not feasible. Users enter credentials in myDBR, which then queries your external service. Implementation details are documented in
user/custom_authentication.php.
For public-facing or internal portals where no login is required, you can configure automatic login credentials. In this mode, administrative access can still be reached by navigating to login.php.
Report Execution
After a successful login, all subsequent database operations are performed using the credentials specified in the Database connection info section of the administration preferences. These credentials (stored in config.php) must have:
- Full access to the myDBR reporting database.
- Read access to the data source databases.
Report Creation
Reports are created as stored procedures within the mydbr database. The configured database user must have execute permissions for these procedures. When querying external databases, reference tables using the following syntax:
- MySQL:
mydatabase.mytable - Microsoft SQL Server / SAP ASE:
mydatabase..mytable
Since SQL Anywhere does not support multiple databases, reports are typically created within the same database as the data. Alternatively, you can use proxy tables to link data from other sources.
Using myDBR with a Read-only Replica
To use myDBR with a read-only replica, install myDBR on the master database for report management and user administration, and point the application to the replica for report execution. This improves performance by offloading heavy reporting queries from the master server.
By default, myDBR writes report statistics and user group synchronization data to the database. To disable these write operations for a replica environment, add the following line to user/defaults.php:
$mydbr_defaults['db_connection']['disable_writes_to_db'] = true;