User Parameters
myDBR reports can include input parameters that prompt the user when the report is executed. These parameters correspond directly to the input arguments of the stored procedure containing the report logic.
Parameters can have default values, which are used during the initial execution. In subsequent runs, myDBR retains the last-used values unless the parameter is configured to ignore the user's previous choices.
Supported parameter types include:
If no specific configuration is provided, myDBR automatically retrieves the parameter names and data types from the stored procedure. It then generates appropriate input fields based on those data types.
Basic Fields (Text/Number)
Basic parameters allow users to enter text or numeric values directly. myDBR allows you to rename these parameters for the user interface, enabling you to provide descriptive titles instead of literal stored procedure variable names.
In this example, we use a film name (or a partial name) as a parameter (in_film_name) in the stored procedure:
create procedure sp_DBR_FilmList( in_film_name varchar(30) )
begin
select title as 'Title',
release_year as 'Release Year',
rental_rate as 'Rental Rate',
length as 'Length'
from mydb.film
where title like concat('%', in_film_name, '%');
end
Once registered, the procedure is ready for execution. By default, the parameter is requested using its variable name:
To provide a more user-friendly label, click the Edit icon () next to the report on the main screen. In the report configuration view, navigate to the parameters section and assign a descriptive name.
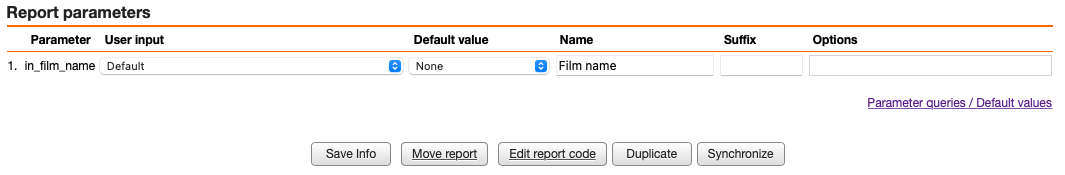
When the report is re-run, the updated parameter label is displayed:
Date Picker
For parameters defined as DATE or DATETIME, myDBR automatically provides a date picker to simplify data entry. The date format follows the user's defined preferences.
If a report requires a date range (e.g., a start and end date), you can display them on the same row. Enable the Keep the next parameter in the same row option for the first date parameter. myDBR will then include a range selector for common intervals (e.g., last week, last month).
create procedure sp_DBR_FilmUpdates( vStartDate date, vEndDate date )
begin
select title as 'Title',
release_year as 'Release Year',
rental_rate as 'Rental Rate',
length as 'Length',
last_update as 'Last Update'
from mydb.film
where last_update between vStartDate and vEndDate;
end
During execution, users are prompted with integrated date selection:
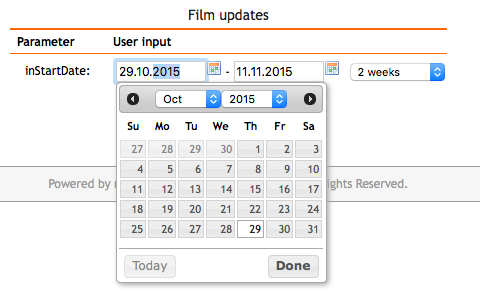
If the parameter type is DATETIME, the picker also includes time selection components.
Default Values
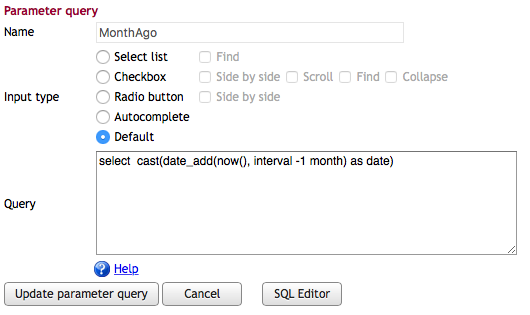
Default values are applied when a report is executed for the first time. For subsequent runs, myDBR uses the user's most recent selections by default. You can define these initial values in the Parameter queries section of the administration tools.
For example, a statistics report might default to showing data for the past month. You can define a default query in Admin -> Parameter queries:
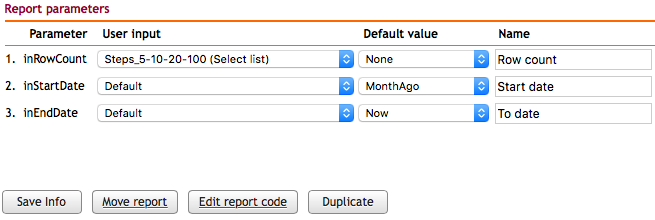
These defaults are then associated with specific parameters in the Edit report screen:
For checkbox parameters, you can provide multiple default values. The default query can either return multiple rows (one for each checked item) or a single comma-separated string. Non-numeric values in a comma-separated list must be enclosed in single quotes (e.g., 'A','B','C').
Predefined and Dynamic Parameters
Rather than allowing free-form input, you can provide users with a list of valid choices. These lists can be static or dynamically generated from your database. Input methods include select lists, radio buttons, and AJAX-based autocomplete fields.
- Radio buttons: Best for small, fixed sets of options.
- Select lists: Ideal for moderate numbers of choices.
- Autocomplete: Recommended for large datasets where users need to search for specific values.
These dynamic parameters are defined as Parameter queries in the administration settings, allowing them to be shared across multiple reports. These queries should return:
- Select list: ID and display value.
- Radio button: ID and display value.
- Autocomplete: Searchable display value.
- Checkbox: ID and display value.
Select Lists
To implement a select list, define a parameter query that returns a set of IDs and their corresponding display names.
A select list query can return the following columns:
ID [, Display Value [, Grouping, [ 'selected' [, Sorting Columns]]]]
- If only one column is returned, it is used for both the ID and the display value.
- Including a Grouping column organizes items into HTML
<optgroup>categories. - Returning
'selected'in the fourth column sets that item as the default choice.
The following example filters a film list based on a category. We use 0 as a special value to display all categories.
create procedure sp_DBR_FilmsByCategory( inCategory tinyint )
begin
select f.title as 'Title',
f.description as 'Description',
f.release_year as 'Release year',
f.rating as 'Rating'
from mydb.film f
where f.film_id in (
select film_id
from film_category
where category_id = inCategory or inCategory = 0
);
end
After defining the parameter query (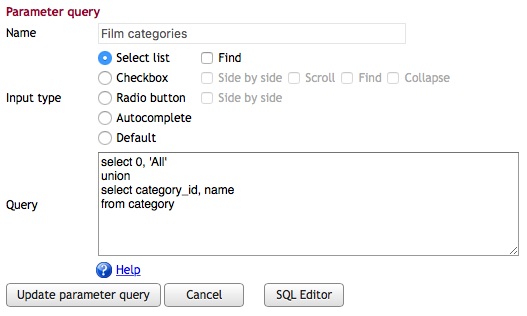 ), attach it to the report parameter in the configuration screen:
), attach it to the report parameter in the configuration screen:
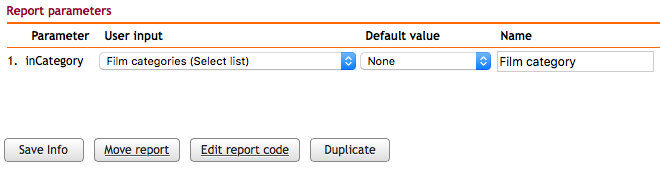
The resulting interface displays the predefined options:
If the query includes a column named parameter_info (at position four or higher), its content, which can include HTML, is displayed as supplemental information for the selected item.
create procedure sp_param_info()
begin
select 1, 'First', '', 'Internal price: 200<br>External price: 300' as 'parameter_info'
union
select 2, 'Second', '', 'Internal price: 250<br>External price: 320'
union
select 3, 'Third', '', 'Internal price: 300<br>External price: 380';
end
Multiselects
Multiselect fields allow users to pick multiple items from a dynamic, AJAX-driven list. myDBR passes these selections to the report as a comma-separated string of IDs.
The multiselect query returns:
ID [, Display Value [, Grouping]]
- If only one column is returned, it serves as both ID and display value.
- A third column defines the
optgroupfor organizational grouping.
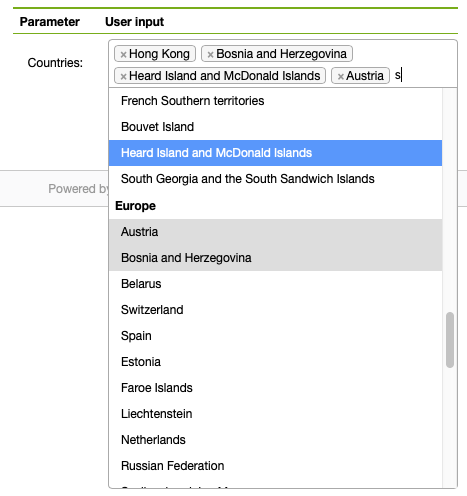
Example of a report filtering by a list of countries (using the MySQL FIND_IN_SET function):
create procedure sp_DBR_FilmsByCategory( in_countries text )
begin
select name
from countries
where find_in_set(id, in_countries);
end
The parameter query for a multiselect must be a stored procedure that accepts the user's search string as an argument. Use LIMIT or TOP to keep the returned list manageable.
create procedure sp_ADBR_multiselect( in_search varchar(255) )
begin
select id, name, continent
from countries
where name like concat('%', in_search, '%')
limit 40;
end
Radio Buttons
Radio buttons function similarly to select lists but display all options simultaneously.
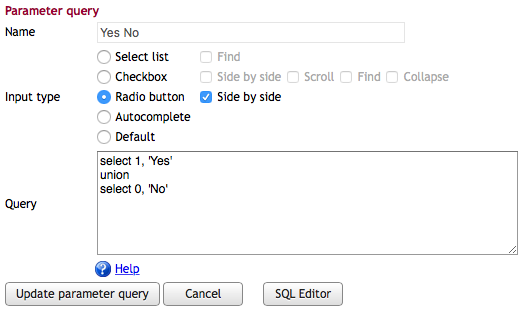
The radio button query returns:
ID [, Display Value [, selected]]
- The second column provides the user-visible label.
- Returning
'selected'in the third or fourth column sets the default choice.
Example procedure:
create procedure sp_DBR_YesNoParam( inYesNo tinyint )
begin
select inYesNo;
end
Execution view:
Checkboxes
Checkboxes allow for multiple simultaneous selections. myDBR delivers the selected IDs as a comma-separated string. The report procedure must parse this string to use the IDs in its logic.
The checkbox query returns:
ID [, Display Value [, Grouping1 [, Grouping2, ... [, 'checked' [, Sorting Columns]]]]]
- Returning
'checked'in a column makes that option selected by default. - Multiple grouping columns can be used to create a hierarchical tree structure.
When a user selects multiple items, a string like "1,2,4,10" (for numeric IDs) or "'A','B','C'" (for strings or dates) is sent. The following MySQL example demonstrates using FIND_IN_SET to filter by the selected checkboxes:
create procedure sp_DBR_checkbox(
inCheckbox varchar(255)
)
begin
select category_id as 'User choice'
from category
where find_in_set(category_id, inCheckbox);
end
For SQL Server 2016 and above, use STRING_SPLIT. For older versions, utilize sp_executesql. SAP ASE users can employ the EXECUTE statement.
Autocomplete Fields
Autocomplete fields provide a text input that performs live database lookups as the user types. This provides suggestions based on actual data, which can be matched using "starts with," "contains," or other logic. The autocomplete source must be a stored procedure.
Single-line Autocomplete
Consider a report that displays film details based on a title search:
create procedure sp_DBR_FilmInfo( inFilmname varchar(30) )
begin
select 'dbr.pageview';
select f.title as 'Title',
f.description as 'Description',
f.release_year as 'Release year',
f.rating as 'Rating'
from mydb.film f
where f.title = inFilmname;
end
The autocomplete procedure accepts the user's input and returns matching titles:
create procedure sp_Autoc_DBR_Titles( inTitle varchar(255) )
begin
select Title
from mydb.film
where Title like concat(inTitle, '%');
end
Multi-line and ID-aware Autocomplete
You can display supplemental information in the autocomplete suggestions by returning a second column.
create procedure sp_Autoc_DBR_Titles( inTitle varchar(255) )
begin
select Title, special_features
from mydb.film
where Title like concat(inTitle, '%');
end
If the autocomplete procedure returns more than two columns, the subsequent values are treated as IDs. You must define matching hidden parameters in your report procedure to capture these IDs. The ID parameters must immediately follow the autocomplete field in the procedure definition.
create procedure sp_DBR_FilmInfo( inFilmname varchar(30), inFilmID int )
begin
select 'dbr.pageview';
select f.title as 'Title',
f.description as 'Description',
f.release_year as 'Release year',
f.rating as 'Rating'
from mydb.film f
where f.film_id = inFilmID;
end
Autocomplete source returning an ID:
create procedure sp_Autoc_DBR_Titles( inTitle varchar(255) )
begin
select Title, special_features, film_id
from mydb.film
where Title like concat(inTitle, '%');
end
Security Note: When using the
inLoginautomatic parameter to filter autocomplete suggestions, always verify the resulting ID within the procedure, as the client-side DOM could be manipulated before submission.
Range Slider
The range slider allows users to select a numeric value or a textual representation between a minimum and maximum bound. It supports both single-value selection and range selection (using the Multiple option, which returns a "min,max" string).
A range query can return:
- A single row with two integers (min and max).
- Multiple rows with a numeric value and its corresponding text label.
File Content
File content parameters allow users to drag and drop files directly into the parameter form. The content of the file (e.g., text, JSON, or XML) is passed as a string parameter. For large files, use the inAutoUsePOST automatic parameter to ensure the form uses a POST request.
Connected Parameters
Connected parameters allow you to create dependencies between input fields. When a user makes a selection in one field (e.g., a car manufacturer), dependent fields (e.g., car models) are automatically updated via AJAX.
Implementation Methods:
- Direct Name Reference: Use the same parameter name in the dependent query's procedure as in the main report procedure. This is the simplest method.
- Relative Addressing: Use keywords like
mydbr_param_prev1ormydbr_param_next1to refer to adjacent parameters. - Fixed Addressing: Use
mydbr_paramX(where X is the parameter index) to refer to a specific parameter by its order.
Example: A three-level hierarchy (Manufacturer -> Model -> Variant).
The main report:
create procedure sp_DBR_car(
inManufacturer int,
inModel int,
inVariant int
)
begin
...
end
Dependent procedure for models:
create procedure sp_ADBR_car_models(inManufacturer int)
begin
select id, name
from car_models
where manufacturer_id = inManufacturer;
end
Automatic Parameters
myDBR provides several automatic parameters that are populated by the system and are not visible to the user. These can be used in reports, default queries, and parameter queries.
- inLogin: The current user's username.
- inIPAddress: The user's IP address.
- inLocale: The user's locale (e.g.,
en_US). - inUseragent: The browser's user agent string.
- inAutoAmIAdmin: Returns
1if the user is an administrator. - inExportFormat: The requested export format (e.g.,
pdf,excel). - inAutoexecute: If set, myDBR runs the report immediately using default parameters.
- inAutoTheme: The user's selected UI theme.
- inAutoUIMode: The current UI mode (
mobileordesktop). - inImportFilename: The name of the file being imported.
- inImportTotalRows: Total number of rows in an import.
- inImportErrors: Number of erroneous rows encountered during import.
- inSessionIDHash: A hash of the user's session ID.
- inAutoUsePOST: Forces the report form to use
POSTinstead ofGET. - GET_[param]: Captures dynamic parameters from the report URL. For example,
&myparam=valueis captured byGET_myparam.
Example: Tracking the Current User
To identify the user executing a report, add inLogin VARCHAR(128) to your procedure parameters. myDBR automatically populates this with the active username.
create procedure sp_DBR_WhoAmI( inLogin varchar(128) )
begin
select 'Report executed by: ', inLogin;
end
Parameters in Linked Reports
When linking reports, you can pass the parent report's input parameters, as well as data from the selected row or chart element, to the child report.
The following example passes both a customer ID (from result data) and a date range (from parent parameters) to a detail report:
Child report (sp_DBR_CustomerRentals):
create procedure sp_DBR_CustomerRentals(inCustomerID int, inStartDate date, inEndDate date)
begin
select f.title as 'Film',
r.rental_date as 'Rental time',
f.rental_rate as 'Rental rate'
from mydb.rental r
join mydb.inventory i on r.inventory_id = i.inventory_id
join mydb.film f on i.film_id = f.film_id
where r.rental_date between inStartDate and inEndDate and r.customer_id = inCustomerID;
end
Parent report mapping:
create procedure sp_DBR_RentalCustomers(inStartDate date, inEndDate date)
begin
select 'dbr.report', 'sp_DBR_CustomerRentals', 'inCustomerID=cid', 'inStartDate=(inStartDate)', 'inEndDate=(inEndDate)';
select concat(c.first_name, ' ', c.last_name) as 'Customer',
count(*) as 'Rentals',
c.customer_id as 'Customer ID[cid]'
from mydb.customer c
join mydb.rental r on r.customer_id = c.customer_id
where r.rental_date between inStartDate and inEndDate
group by c.customer_id, Customer;
end
In this mapping:
inCustomerID=cid: TheinCustomerIDparameter is populated from thecidcolumn.inStartDate=(inStartDate): TheinStartDateparameter is inherited from the parent report's input.
For more information, refer to the Report Linking section.