Cross-tabulation
Commands
dbr.crosstab - Turns a result set into a cross-tabulation report. The first parameter is the crosstab column; the optional second parameter marks the last data column within the crosstab.
dbr.hsum - Calculates the horizontal sum in a cross-tabulation report
dbr.hmin - Calculates the horizontal minimum in a cross-tabulation report
dbr.hmax - Calculates the horizontal maximum in a cross-tabulation report
dbr.hminus - Calculates horizontal values using the formula Col1 - Col2 - Col3...
dbr.hnull - Creates a placeholder for a horizontal column used with dbr.calc
dbr.hcount - Calculates the number of values horizontally in a cross-tabulation report
dbr.havg - Calculates the horizontal average in a cross-tabulation report
dbr.hidecolumn.data - Hides crosstab data columns while keeping the summary column. Used with dbr.calc
dbr.hidecolumn.set.data - Hides crosstab data columns based on the CrossTabSet name
dbr.hidedatacolumn - Same as dbr.hidecolumn.data, kept for backwards compatibility
dbr.hidecolumn.data.all - Hides all crosstab data columns while keeping the summary column
dbr.hidecolumn.summary - Hides crosstab summary columns while keeping data columns. Used with dbr.calc
dbr.crosstab.title - Overrides the default title for the horizontal summary column
dbr.crosstab.order - Sets the order of the cross-tabulation columns
dbr.crosstab.col - Predefines the cross-tabulation columns
dbr.crosstab.options - Adds a crosstab option
dbr.crosstab.col.title - Sets the column title for the crosstab horizontal summary column
dbr.crosstab.col.style - Sets the column style for the crosstab horizontal summary column
dbr.crosstab.header - Adds an additional header group to the crosstab
dbr.crosstab.header.col - Predefines the 2nd-level cross-tabulation header columns for dbr.crosstab.header
dbr.crosstab.group - Groups crosstab column values by adding another header level
dbr.crosstab.data.tooltip - Defines a crosstab header tooltip based on the crosstab data value
Syntax
select 'dbr.crosstab', ColumnReference [, ColumnReference]
select 'dbr.hsum', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hmin', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hmax', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hminus', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hnull', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hcount', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.havg', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hidecolumn.data', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hidecolumn.set.data', 'CrossTabSet', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hidedatacolumn', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.hidecolumn.data.all' {, 1/0 }
select 'dbr.hidecolumn.summary', ColumnReference, [ColumnReference... ]
select 'dbr.crosstab.title', 'title'
select 'dbr.crosstab.order', 'asc'|'desc'
select 'dbr.crosstab.col', col_value1, [col_value2... ]
select 'dbr.crosstab.options', 'no_null_data' | 'summary_first'
select 'dbr.crosstab.col.title', ColumnReference, 'title'
select 'dbr.crosstab.col.style', ColumnReference, columnstyle
select 'dbr.crosstab.header', ColumnReference
select 'dbr.crosstab.header.col', col_value1, [col_value2... ]
select 'dbr.crosstab.group', 'crosstab_value', 'group_name'
select 'dbr.crosstab.data.tooltip', 'crosstab_data_value', 'tooltip'
Syntax Tips
Where:
- dbr.crosstab.options
Options for crosstabno_null_dataSuppresses null crosstab columns generated by, for example, a LEFT JOINsummary_firstShows the horizontal summary columns before the data columns. Useful when there is a large number of data columns.
Explanation
In the context of cross-tabulation, the data in the result set is organized into distinct header and data sections, separated by a designated cross-tabulation column. Header columns, positioned to the left of the cross-tabulation column, determine the unique rows within the final result set. On the right side of the cross-tabulation column, data columns---derived from the cross-tabulation---will be displayed. When using the dbr.crosstab command, you can specify a second parameter to include header columns on both sides of the cross-tabulation data columns.
Examples
Consider the following basic data set:
select RepArea as 'Reporting area',
Period,
last_year as 'Last year',
this_year as 'This year',
next_year as 'Next year'
from mydb.ProductionSummary;
We can determine the different parts of the result set:
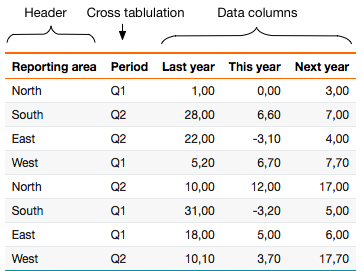
When the 'Period' column is designated as the cross-tabulation column, its unique values become group headers, with data columns arranged beneath each.
/*
Define the Period as a cross-tabulation column
*/
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Period';
select RepArea as 'Reporting area',
Period,
last_year as 'Last year',
this_year as 'This year',
next_year as 'Next year'
from mydb.ProductionSummary;
Calculating Column and Row Summaries
You can apply aggregate functions to both row and column values. For columns, use functions such as dbr.sum, dbr.min, dbr.max, dbr.avg, or dbr.count. For rows, use dbr.hsum, dbr.hmin, or dbr.hmax.
myDBR streamlines the calculation process by performing computations on relevant columns and adding summary columns when necessary. If a data column is unnamed (set to an empty string), the corresponding header section will be hidden (refer to the example below).
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Quarter';
select 'dbr.sum', 'Items','Weight';
select 'dbr.crosstab.title', '2008 total';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'Items','Weight';
select Name,
concat(year(InsertDate), ' Q',quarter(InsertDate)) as 'Quarter',
sum(Items) as 'Items',
sum(Weight) as 'Weight'
from mydb.Production
group by Name, 2;
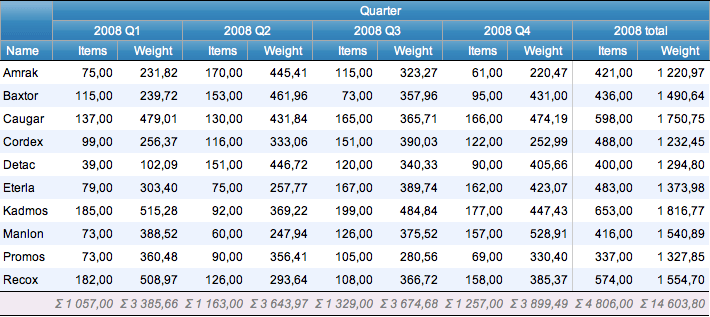
You can calculate multiple horizontal aggregates for a column by duplicating the column and hiding the data column. The data column refers to the repeated cross-tabulation data column. In the example, multiple horizontal aggregates are calculated and styled:
/* Set titles for horizontal aggregate columns */
select 'dbr.crosstab.col.title', 'value', 'Avg';
select 'dbr.crosstab.col.title', 'sum', 'Sum';
select 'dbr.crosstab.col.title', 'count', 'Count';
/* Style the horizontal average column */
select 'dbr.crosstab.col.style', 'value', '[color:red]%.1f';
/* Style the horizontal sum column */
select 'dbr.crosstab.col.style', 'sum', '[color:green]';
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Quarter';
/* Horizontal aggregates */
select 'dbr.havg', 'value';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'sum';
select 'dbr.hcount', 'count';
/* Show the sum and count columns only in the horizontal summary section */
select 'dbr.hidecolumn.data', 'sum';
select 'dbr.hidecolumn.data', 'count';
/* Vertical aggregates */
select 'dbr.sum', 'value';
select 'dbr.sum', 'sum';
select 'dbr.sum', 'count';
select
Name,
concat('Q',quarter(InsertDate)) as 'Quarter',
sum(Items) as '[value]',
sum(Items) as '[sum]',
sum(Items) as '[count]'
from TestTable
group by Name, 2
order by Name, 2;
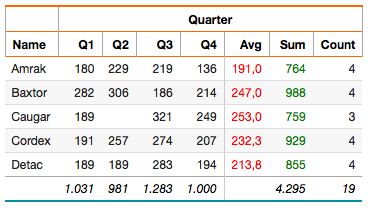
Define the Crosstab Column Header Order
To define the order of existing cross-tabulation column headers, use the dbr.crosstab.order command.
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Month';
select 'dbr.crosstab.order', 'asc';
select 'dbr.sum', 'value';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'value';
select Name,
Month,
Value as '[value]',
from mydb.monthlyvalues
order by Name;
If your data lacks certain cross-tabulation column headers that you want to display in the report, use the dbr.crosstab.col command.
Predefine data columns
Predefining the data columns allows you to specify which columns are displayed in the cross-tabulation report and in what order. This is particularly useful when you have a predefined set of cross-tabulation columns you want to include in the report (such as a series of months or fixed quarters) or when you wish to include columns that do not exist in the original data.
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Month';
select 'dbr.sum', 'value';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'value';
select Name,
Month,
Value as '[value]',
from mydb.monthlyvalues
order by Name;
In this example, we generate a report with a monthly distribution. Note that the data may not cover all months (1–12).
In this example, the months were derived from the fetched data, reflecting their order and actual values. However, if you need to explicitly define all months (1–12) and control the column order, you can do so using the dbr.crosstab.col command.
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Month';
select 'dbr.crosstab.col', 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12;
select 'dbr.sum', 'value';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'value';
select Name,
Month,
Value as '[value]',
from mydb.monthlyvalues
order by Name;
The result shows all months explicitly defined and arranged in order.
When you have a dynamic number of columns (such as when the report parameter involves a date range), you can call dbr.crosstab.col multiple times. Each call adds further columns to the report.
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Month';
declare iMonth int;
set iMonth = 1;
while( iMonth <= inMonthParameter ) do
select 'dbr.crosstab.col', iMonth;
set iMonth = iMonth + 1;
end while;
select 'dbr.sum', 'value';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'value';
select Name,
Month,
Value as '[value]',
from mydb.monthlyvalues
order by Name;
If the report query generates data columns that are not explicitly defined in the predefined data columns, these additional columns will be appended to the end of the column list.
Add a Second Crosstab Level
To add a second crosstab level based on the data:
select 'dbr.crosstab.header', 'Year';
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Quarter', 'Items';
select 'dbr.sum', 'Items';
select
Name,
year(InsertDate) as 'Year',
concat('Q',quarter(InsertDate)) as 'Quarter[Quarter]',
sum(Items) as '[Items]
from data
group by Name, Year, 3
order by Name, Year, 3;
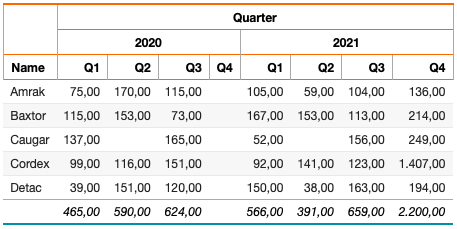
Add a Second Crosstab Header Row
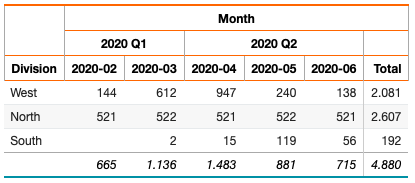
You can add a second crosstab level header row:
select distinct 'dbr.crosstab.group',
date_format(InsertDate, '%Y-%m'),
concat(date_format(concat(InsertDate,'-01'), '%Y Q'), QUARTER(concat(InsertDate,'-01'))) as 'Quarter'
from data;
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Month';
select 'dbr.sum','Value';
select 'dbr.hsum','Value';
select Division, date_format(InsertDate, '%Y-%m') as 'Month', Value as '[Value]'
from data;
Crosstab Linked Report
Linked reports can be attached to any column in the table except the crosstab column. Any column can be used as a linked report parameter. If a linked report is attached to a crosstab data column, the report is invoked for each repeated data item.
select 'dbr.report', 'sp_DBR_show_count', 'popup', '[value]', 'inID=id', 'inCnt=cnt';
select 'dbr.report', 'sp_DBR_show_count', 'popup', '[value.h]', 'inID=id', 'inCnt=cnt.h';
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'ct', 'cnt';
select 'dbr.sum','value';
select 'dbr.hsum','value';
select 'dbr.hsum','cnt';
select 'dbr.hidecolumn', 'cnt';
select
1 as id,
'Sammple crosstab' as title,
'Q1' as '[ct]',
1200 as value,
11 as cnt,
'last column'
union
select
1,
'Sammple crosstab',
'Q2',
2300,
12,
'last column';
The report output:
Internally, the data looks like this (without the hidden 'cnt' column):
The first linked report targets the value column with two parameters: id and cnt. Since the id column precedes the repeated data columns, all instances of inID receive the same value (1). The cnt column is within the data column set, giving distinct values (11 for Q1 and 12 for Q2). When a user clicks the value from Q2 (=2300), myDBR calls sp_DBR_show_count(1, 12).
The second linked report targets the horizontal summary column value.h. The reference cnt.h corresponds to the cnt value of 23 in the horizontal summary column. When a user clicks the horizontal summary value (3500), myDBR calls sp_DBR_show_count(1, 23).
Full Cross-tabulation Example
When the 'Period' column is designated as the cross-tabulation column, its distinct values become group headers, with data columns arranged beneath each.
/*
Define the Period as a cross-tabulation column
Add column and horizontal sums
Name the crosstab column
*/
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Period';
select 'dbr.sum', 'last', 'this', 'next';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'last', 'this', 'next';
select 'dbr.crosstab.title', 'Total H1';
select 'dbr.summary.text', 'area','Total';
select RepArea as 'Reporting area[area]',
Period,
last_year as 'Last year[last]',
this_year as 'This year[this]',
next_year as 'Next year[next]'
from mydb.ProductionSummary;
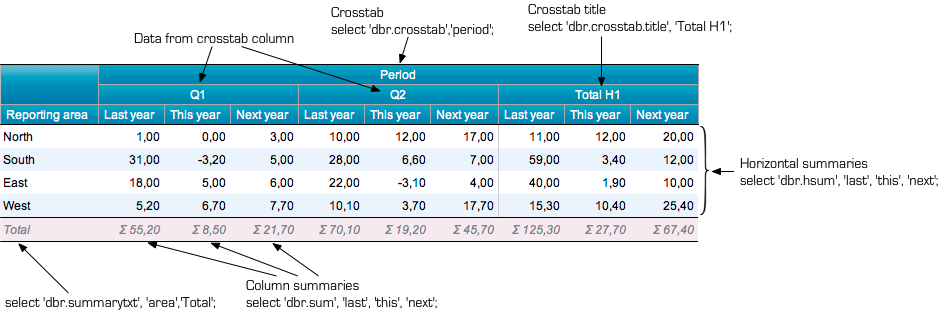
The second parameter of dbr.crosstab specifies the last data column within the cross-tabulation. Columns after this position are placed outside the crosstab section.
/*
Define the Period as a cross-tabulation column and 'next' column to be the last data column inside the cross-tabulation.
*/
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'Period', 'next';
select 'dbr.sum', 'last', 'this', 'next';
select 'dbr.hsum', 'last', 'this', 'next';
select 'dbr.crosstab.title', 'Total H1';
select 'dbr.summary.text', 'area','Total';
select RepArea as 'Reporting area[area]',
Period,
last_year as 'Last year[last]',
this_year as 'This year[this]',
next_year as 'Next year[next]'
Optional
from mydb.ProductionSummary;
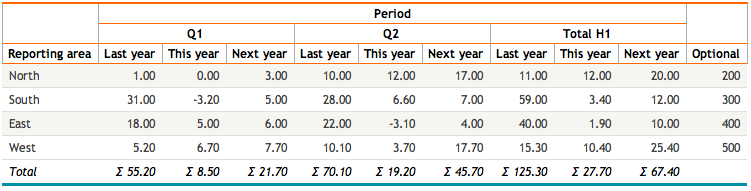
The no_null_data option suppresses null crosstab columns that are often produced by operations such as LEFT JOIN. The row is still displayed (if other rows contain data), but the NULL column is omitted as a crosstab data column.
In the example, rows are created for each month even if no rate is specified for the hotel in that month. The no_null_data option ensures that the NULL column, generated by the crosstab column 'name' due to the LEFT JOIN, is suppressed.
create temporary table d (
d date
);
insert into d values ('2016-01-01'),('2016-01-02'),('2016-01-03');
select 'dbr.crosstab', 'name';
select 'dbr.crosstab.options', 'no_null_data';
select d.d as 'Day', h.name as '[name]', h.rate as ''
from d d
left join (
select cast('2016-01-02' as date) as d, 'The Imprerial' as name, 680 as 'rate'
from mydbr_version
) as h on h.d=d.d
order by d.d;